About lumbar spinal canal stenosis
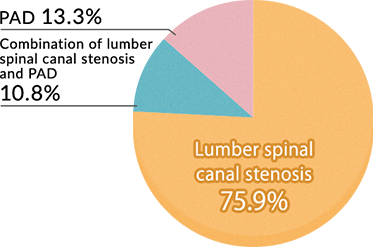
Intermittent claudication may be caused either by lumbar spinal canal stenosis or by peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
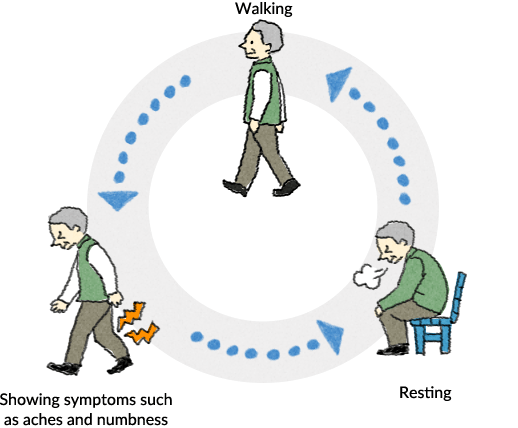
Intermittent claudication refers to the situation in which walking becomes impossible due to pain and numbness in the feet/legs after walking a short distance and then being able to resume walking after resting for a while. The leading causes of intermittent claudication are lumbar spinal canal stenosis, which is a disease of the nerves in the lower back, and PAD, which is a disease of the blood vessels in the feet/legs.
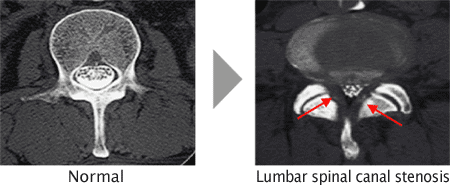
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis is the compression of nerves in the spine of the lower back.
In lumbar spinal canal stenosis the spine in the lower back degenerates, narrowing the spinal canal-the path through which nerves in the spine passes. Narrowing of the spinal canal puts pressure on the nerves inside, causing numbness and pain in the legs and lower back.
Difference between lumbar spinal canal stenosis and PAD
| Lumbar spinal canal stenosis | PAD | |
|---|---|---|
| Experience pain when standing still | Yes | No |
| Experience pain when riding a bicycle | No | Yes |
| Experience pain when leaning forward | Yes | No |
| Pulse in the legs | Can be found | Weak or cannot be found |
Aging is the main cause of lumbar spinal canal stenosis.
Degeneration of the lumbar vertebrae that occurs with aging is the main cause of lumbar spinal canal stenosis. It is a disease in which damaged joints and disks and thickened ligaments put pressure on the nerves as if choking them.
Symptoms of lumbar spinal canal stenosis include leg pain and numbness in addition to intermittent claudication.
Symptoms of lumbar spinal canal stenosis include pain and numbness in the lower back, buttocks, back of the thighs, and calves in addition to intermittent claudication. The legs may also feel weak. Severe cases may be accompanied by paralysis of the legs and loss of bladder and bowel control.
The basic treatments for lumbar spinal canal stenosis are drugs, rehabilitation, and injection therapy.
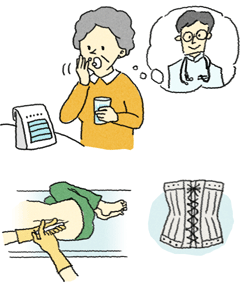
The first line of treatment for lumbar spinal canal stenosis is treatment using drugs that reduce pain, improve circulation, or relax the muscles.
Depending on the symptoms, a corset may be used to ease the burden on the lower back. Heat therapy, in which heating the affected area to improve blood circulation and relax the muscles alleviates the pain, and exercise therapy consisting of stretching and muscle-building exercises may also be used.
An injection therapy called nerve block is also effective. If these treatments do not produce an improvement and if the condition is interfering with everyday life, surgery may be performed to cut out the bone deformity that is the cause of the stenosis.






