Effects of an amino acid-carbohydrate drink on exercise performance after consecutive-day exercise bouts
Skillen RA, Testa M, Applegate EA, Heiden EA, Fascetti AJ, Casazza GA,
Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exer. Met 2008; 18: 473-492
Objective
To examine the effects of continued ingestion of drinks containing BCAA on exercise performance over consecutive days.
Methodology
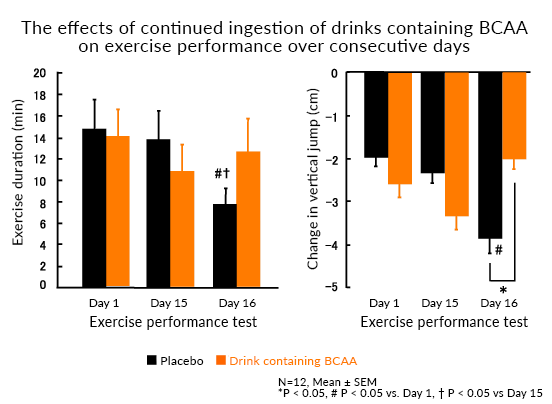
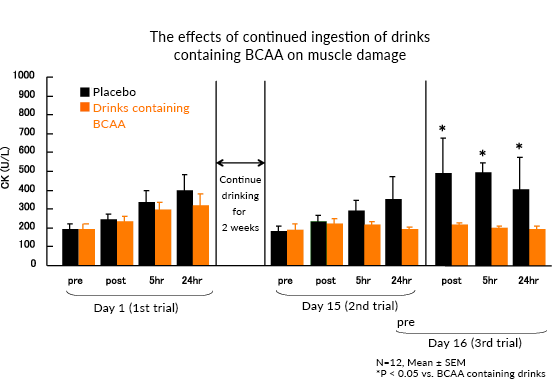
12 male cyclists were given either a drink containing BCAA (4g/500mL) or an isocaloric placebo drink, and a double-blind crossover study performed. The subjects were given the drink containing BCAA every day for two weeks and performed a cycling exercise (at 75% V02 peak for 90 minutes, followed by a ride to exhaustion at 85% of VO2 peak intensity), as a test of exercise performance on the first day of the regimen as well as on the 15th and 16th days. Exercise duration was measured as an indicator of performance, vertical jump as an indicator of muscle fatigue, and CK (creatine kinase) activity as an indicator of muscle damage. The effects of a single intake of the BCAA-containing drink on the first day of the regimen, the effects of continued intake (for two weeks) on the 15th day, and the effects of exercising on consecutive days on the 16th day were assessed.
Results
The results of the exercise performance tests showed significant declines in exercise duration from consecutive bouts of exercise over two days when taking the placebo drink, whereas no such decline was observed while taking the drink containing BCAA. Regarding changes in vertical jump, an indicator of muscle fatigue, significant declines were found in the records when taking the placebo, while no such declines were observed while taking the BCAA-containing drink. Declines in the vertical jump records were suppressed significantly when taking the drink containing BCAA compared to the placebo drink. Furthermore, the decline in CK activity induced by consecutive bouts of exercise over two days was significantly inhibited when taking the drink containing BCAA compared to the placebo.
Conclusions
Exercise performance when exercising over consecutive days was maintained, and muscle fatigue and damage diminished due to continued ingestion of the drink containing BCAA. These results suggest that continuous ingestion of BCAA is effective for maintaining exercise performance and condition in competitive sports where daily training and games/matches are prolonged.