Basic Acne Knowledge
Acne is a more complicated disease than people think, with multiple causes including sebum (oil secreted from pores), clogged pores and Propionibacterium acnes.
The main causes of acne include:
The symptoms we usually call acne are a skin disease called acne vulgaris.
Acne - the red bumps that frequently appear on the face, chest, and back - is a condition in which hair follicles (sac-like parts of the skin at the roots of hairs) and sebaceous glands are inflamed.
The main causes of acne include:
- 1Excess sebum production
- 2Hyperkeratinization (a disorder of the cells) of the exit of pores resulting in clogging
- 3Proliferation of propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria
P. acnes (Propionibacterium acnes)
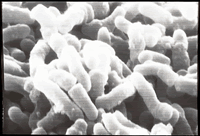
Photo: Setsuko Nishijima
The progression of acne
There are several stages in the development of acne. This is how acne worsens around an infected pore.
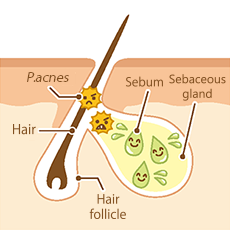
P. acnes can be found even in normal pores.
Sebum produced in sebaceous glands is excreted from pores up to the surface of the skin.
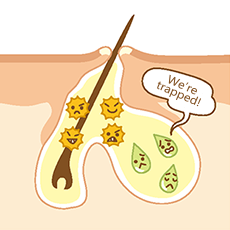
If abnormal keratinization occurs near the exit of a pore, the pore becomes blocked, trapping sebum inside (referred to as a comedo).
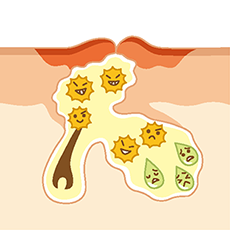
When sebum builds up, P. acnes, which live primarily on fatty acids in the sebum, increase. P. acnes produces a variety of substances that cause inflammation, resulting in a reddish inflammation (papules).
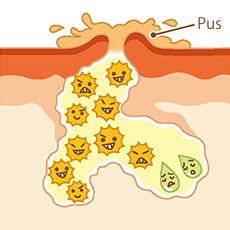
As the inflammation advances, the wall of the widened pore breaks, causing the inflammation to spread and pus to exude (pustules).
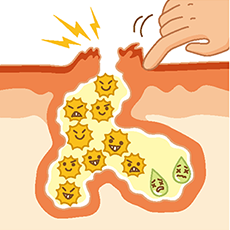
Popping pimples or having your hair constantly rub against your face irritates acne, causing it to worsen further.
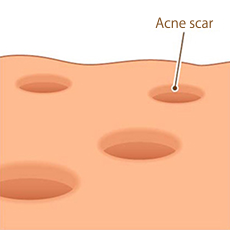
If acne gets worse, it may leave scars after it has healed (cicatrice).
Acne peaks during puberty
Acne's peak age of onset occurs during puberty and gradually decreases in adulthood. In women it is frequently seen until after midlife. There is said to be little gender difference in the onset of acne, but nearly twice as many women as men consult a doctor for help with dealing with it.
Types of acne and when they appear
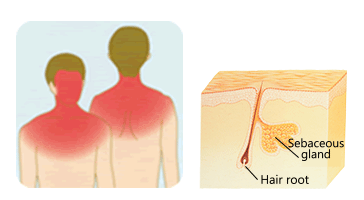
Pores with large sebaceous glands are distributed throughout the face, chest, and back (the red areas in the illustration above). Sebum excreted from sebaceous glands maintains skin moisture. Acne (acne vulgaris) is a disease that occurs in these sebaceous follicles.
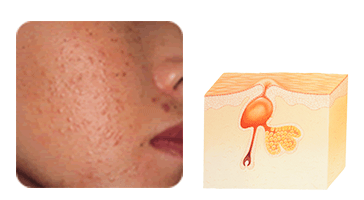
A comedo is an enlarged pore that has been plugged and clogged with sebum. Bacteria like P. acnes tend to thrive in these conditions.
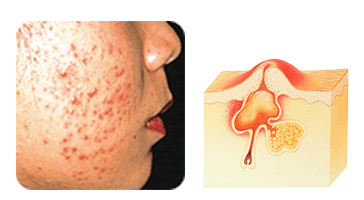
A papule is an inflamed, solid elevation of skin. If it becomes more severe it develops into a pustule.
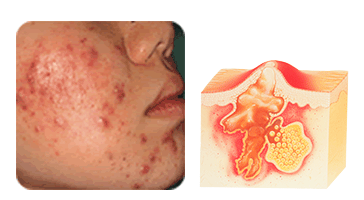
A pustule is a more severe form of papule in which the pore has broken. P. acnes proliferates, pus accumulates, and inflammation worsens.
Photo: Setsuko Nishijima
In order not to leave scars, it's important to tame the inflammation at an early stage. It's recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible.






