Indigestible dextrin
Indigestible dextrin is made from corn, and is used in supplement foods designed to prevent dietary fiber deficiency.
It is also approved as a functional ingredient of 'food for specified health use' by the Consumer Affairs Agency (Japan).
What is indigestible dextrin?
Indigestible dextrin: created to prevent dietary fiber deficiency
Dextrin is a general term for substances that have been polymerized*1 by glycosidic bonds*2 of several alpha-glucose molecules. Dextrins are a type of starch, and as the name suggests, indigestible dextrin resists digestion. Dextrin is made from cornstarch that is roasted and then hydrolyzed by amylase (an enzyme that digests starch taken in as food). Indigestible dextrin is a water-soluble dietary fiber extracted and prepared from the indigestible components in the resulting mush.
Dextrin was created with the aim of supplementing dietary fiber, which tends to be deficient in many diets. . The aqueous solution of dextrin, which has low viscosity and low sweetness, is a food ingredient that is nearly transparent with excellent heat and acid resistance.
Its many different physiological functions make it suitable for use in a variety of foods.
- *1Polymerization: the formation of a different compound with a large molecular weight through the bonding of two or more molecular compounds with a simple structure.
- *2Glycosidic bond: a structure that joins the sugar units in polysaccharides.
Is indigestible dextrin safe?
The FDA has approved indigestible dextrin (which has been used as an ingredient in foods for a long time), as an ingredient that is so safe that there is no need to establish a daily intake limit. Additionally, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved the labeling of certain functions as a "Food for Specified Health Use" and acknowledges the safety of indigestible dextrin.
In a past human study that investigated safety, no adverse effect whatsoever was seen in physiological tests monitoring blood pressure etc. after subjects took 10 grams of indigestible dextrin three times daily before meals for 16 weeks. It was also reported that no changes were seen in laboratory test values, in particular in the concentration of serum protein and minerals such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and iron (Fe), as a result of the intake of indigestible dextrin.
Furthermore, no symptoms that could be particularly problematic, including gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, were seen during the study period, leading to the report that indigestible dextrin is safe.
Source: The Japanese Journal of Clinical Nutrition Vol. 83, No. 3: P301-305; 1993
How indigestible dextrin works in the body
Indigestible dextrin has five main actions:
1.Slows sugar absorption (suppresses post-meal blood sugar rise)
Sugars taken in from food are broken down into glucose inside the body. In several trials on sugars conducted in rats and humans, indigestible dextrin, along with monosaccharides and disaccharides, was confirmed to have no effect on monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose while it did act to suppress blood sugar rise caused by maltose.
Indigestible dextrin suppresses the rise of blood sugar after meals by inhibiting the digestion of maltose.
Further, human studies in which indigestible dextrin was taken together with meals confirmed that it suppresses the rise of blood sugar after eating.
Sources:
Endocrine Journal (The Japan Endocrine Society) 68: 623-635 (1992)
Journal of the Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science 46: 131-137 (1993)
Journal of the Japan Diabetes Society 35: 873-880 (1992)
The Japanese Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics 53: 361-368 (1995)
Journal of the Japanese Association for Dietary Fiber Research 3: 13-19 (1999)
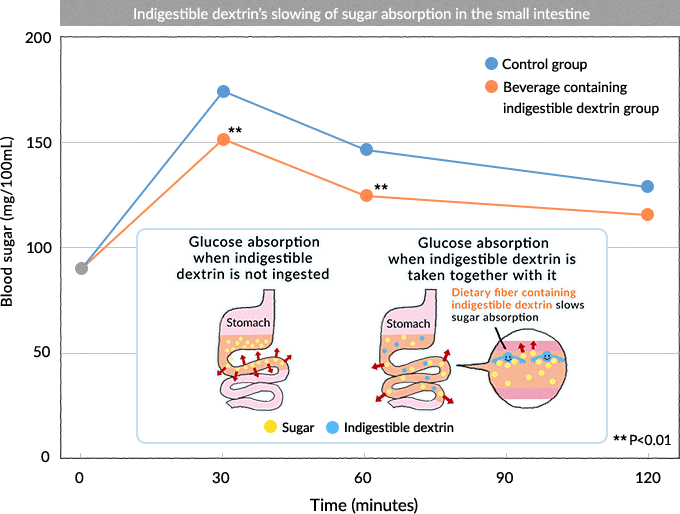
When 36 subjects were given tea mixed with 5 grams of indigestible dextrin together with an udon noodle meal, the rise in their blood sugar was suppressed significantly compared to when they were given normal tea.
2.Intestinal healing effect
Indigestible dextrin has been found to have beneficial effects on the intestines, such as improving intestinal flora.
It has been reported that past human studies found that indigestible dextrin caused increases in the amount of stool and the frequency of bowel movements.
Taking 5 or 10 grams of indigestible dextrin per day resulted in increased frequency of bowel movements and the amount of stool as well as making hard stools soft and increasing comfort after defecation.
Source: The Japanese Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics Vol.51, No.1: P31-37; 1993.
3.Slows fat absorption (suppresses post-meal triglyceride rise)
When taken together with a meal, indigestible dextrin slows the absorption of fats in the food, acting to lessen the rise of triglycerides after eating.
Source: Japanese Pharmacology & Therapeutics Vol. 36, No. 5: P445-451; 2008
4.Reduction of visceral fat
In a study in which 36 adult men with a BMI of 23 or higher took a tea beverage containing 9 grams of indigestible dextrin or normal tea, a significant decrease in visceral fat and triglycerides was confirmed in the group that took the indigestible dextrin.
Source: Obesity Research Vol. 13, No. 1: P34-41: 2007
5.Promotion of mineral absorption
Animal studies have confirmed that indigestible dextrin promotes the absorption of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn). Also, when female university students with low serum iron took 15 grams of indigestible dextrin for four weeks, their serum iron levels increased, improving their conditions.






