The role of nutrients and nutrient consumption
Nutrients are essential for the body
Nutrient roles
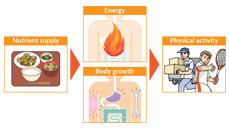
Our bodies are built of and powered by solely what we eat and drink. Food is the source of all of the energy needed Why do humans have to eat? Is it just because we get hungry? That is not all. People get energy from food. We need energy all the time, when we run, jump, sing, and even when we sleep. We create all the energy we need by eating. The structures components that make up the human body, such as muscles, organs, and bones, are also composed of the nutrients contained in food, meaning that it is. This is why eating and taking in the nutrients that provide energy and become the components of our bodily structures is essential to for sustaining human life.
Editorial supervision: Yuki Sugishima (National Registered Dietician/ Certified Sports Dietician*), Assistant Professor, Shigakkan University, Faculty of Wellness, Department of Nutrition
- *Joint certified by The Japan Dietetic Association and The Japan Sport Association
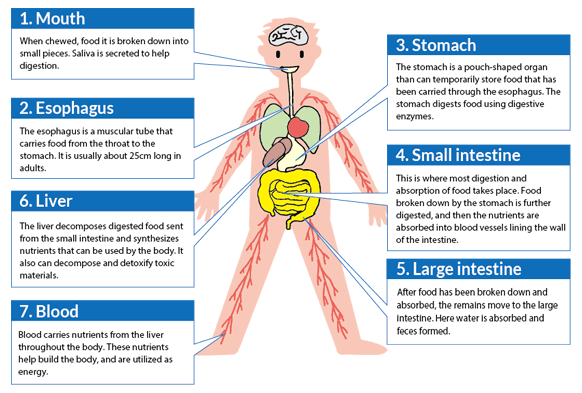
The roles of the five major nutrients
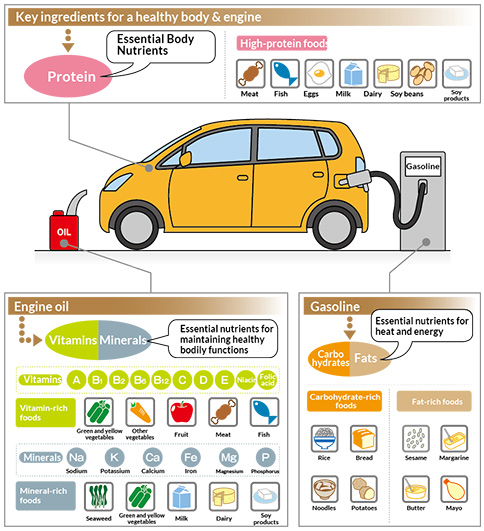
Nutrients are the substances found in food which drive biological activity, and are essential for the human body. They are categorized as proteins, fats, carbohydrates (sugars, dietary fiber), vitamins, and minerals, and perform the following vital functions.
- 1Building all parts of the body such as muscle, bone, teeth, and blood
- 2Producing energy (power and heat)
- 3Keeping the body in good working order
the building blocks of the body
Proteins: the building blocks of the body
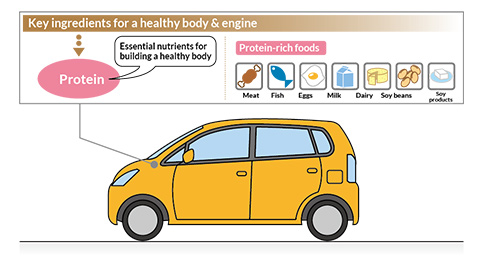
Protein is the main constituent of the body, making up the muscles, internal organs, skin, and blood, etc. If compared to a car, it would be the material from which the body and engine are made. Just like a car cannot be driven fast without a solid frame, without protein the human body cannot be kept in a healthy state. There are 20 kinds of amino acids that make up proteins, 9 of which are not synthesized in the body, and are therefore called essential amino acids. These essential amino acids must be supplemented from meals.
the body's energy (power and heat) source
Fats/carbohydrates (sugars): the body's energy (power and heat) source
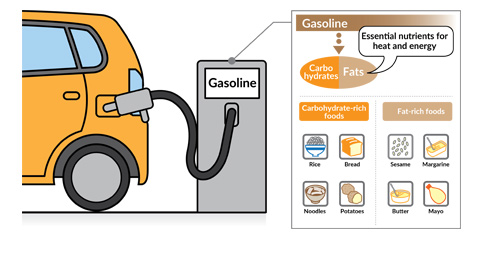
Although consuming too much fat can lead to obesity, small amounts can provide a highly efficient energy source (9kcal per gram). Carbohydrates can be broken down further into the two categories of sugars and dietary fiber. Sugars are the carbohydrates which can be used as an energy source to move the body (such as during exercise) and are stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen. Sugars are also the main source of energy for the brain. Dietary fiber, on the other hand, is also known as the sixth major nutrient and is the indigestible portion of food that is not broken down by human digestive enzymes. It helps to increase the number of good bacteria in the digestive tract, maintain the balance of bacteria in the intestines, and as such is very beneficial for the body. Fats can be found in abundance in the fatty portion of meats and in cooking oils, and sugars can be found in ample quantities in grains, potatoes, sugar, and fruit.
keeping the body in good working order
Vitamins/minerals: keeping the body in good working order
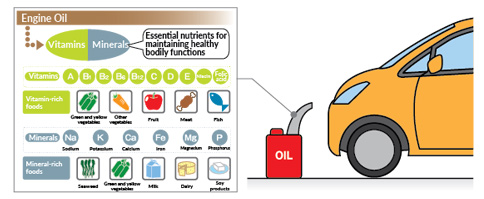
Vitamins and minerals are not used as energy, but instead aid in breaking down and building up proteins, fats, and sugars, and are an essential nutrient for keeping the body healthy and in good working order. "Vitamin" is the general term for the organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) which are mostly impossible for the body to synthesize, and a lack of these vitamins can possibly lead to various deficiency-related diseases. Vitamins can be broken down into two categories: water-soluble and fat-soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) dissolve easily in fats and can lead to a vitamin overdose if consumed in large amounts. Water-soluble vitamins (B vitamins, C) dissolve easily in water and thus carry very little risk of overdose. Vitamins can be found in large amounts in fruit and vegetables.
"Mineral," also referred to as inorganic matter, is a general term for the chemical elements which make up the human body excluding oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen. There are 16 different minerals which are necessary for the human body, including calcium, iron, and sodium, and they can be found in abundance in fruit, vegetables, seaweed, and milk/dairy products.