Branched-chain amino acid supplementation increases the lactate threshold during an incremental exercise test in trained individuals
Matsumoto K, Koba T, Hamada K, Tsujimoto H, Mitsuzono R
J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol 2009; 55: 52-58
Objective
To examine the effects of ingesting drinks containing BCAA on the lactate threshold (LT).
Methodology
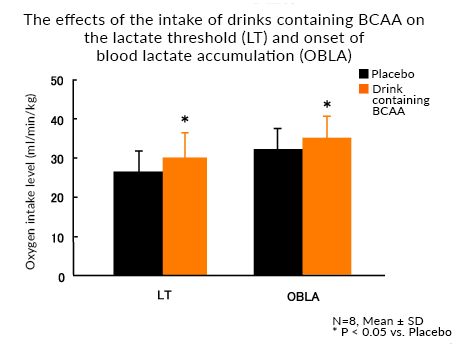
Eight trained male subjects were given either a drink containing BCAA (2g/500mL) or an isocaloric placebo drink, and a double-blind crossover study was performed. The subjects were given three bottles of either the drink containing BCAA (6g/day) or the placebo drink for six days before taking an incremental load exercise test* conducted using a cycling exercise on the seventh day. The subjects were given one bottle of the BCAA-containing drink or the placebo drink 15 minutes before the incremental load exercise test. Blood and oxygen samples were taken over time before consuming the drinks as well as during the exercise, and blood lactate, amino acid concentrations, and oxygen intake levels were measured. LT and OBLA (onset of blood lactate accumulation: corresponds to 4mmol of lactic acid/L), better indicators of the endurance capacity than fluctuations in blood lactate concentrations and oxygen intake, were also calculated.
- *Incremental Load Exercise Test: A test wherein resistance is gradually increased while repeating constant load and rest intervals.
Results
Blood BCAA concentrations during exercise were higher while taking the drink containing BCAA compared to the placebo drink. The points at which LT and OBLA were reached were significantly higher when taking the BCAA-containing drink compared to the placebo.
Conclusions
Continued intake of the drink containing BCAA elevated the LT and OBLA, which are indicators of endurance capacity, thus suggesting that drinks containing BCAA drinks may enhance endurance.