Carbohydrates: an efficient energy source
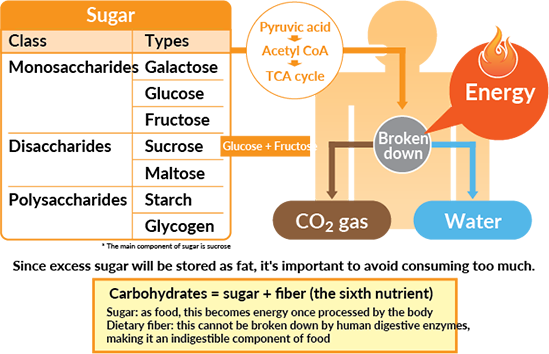
Carbohydrates are the nutrients most frequently used as an energy source (containing 4kcal per gram), as they are fast-acting and turn into energy as soon as they are ingested. This energy powers the brain and body.
The energy that powers the brain and body is generated when carbohydrates are broken down.
How much should you eat?
Cereals, potatoes, fruits, and sugars are rich in carbohydrates.
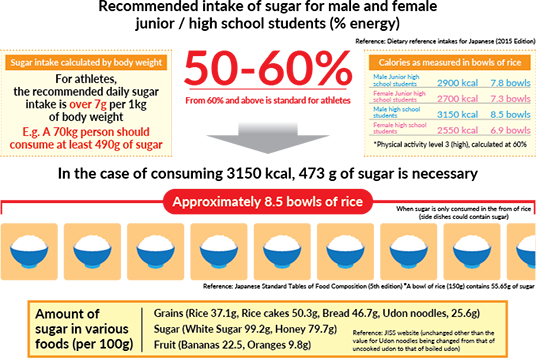
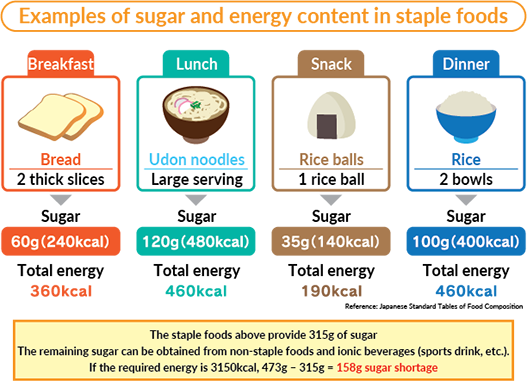
For example, junior and senior high school students, who are more active when doing sports than older people, need to ingest the equivalent of the amount of carbohydrates contained in about 8.5 cups of rice per day*.
- *When converting only the volume of rice, without considering side dishes (grains, potatoes, etc.), fruits, sugars, etc.
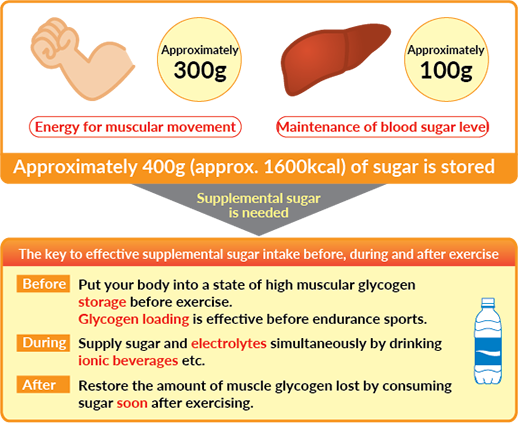
How much carbohydrate is in the body?
Unlike fats, only a small amount (about 400 grams) of carbohydrates can be stored in the body.
Therefore, it is necessary to supplement it by eating before, during, and after exercise.
Ion drinks for supplementing sugar during exercise
According to the guidelines of the American College of Sports Medicine, "it is considered desirable to ingest 30 to 60 grams of sugar per hour to prevent fatigue." For example, if a 6% sugar ionic beverage (sports drink) is ingested during exercise, you will get 30 grams from a 500 ml bottle and 60 grams from 1 liter. Ionic drinks allow you to ingest not only water, but also sugar, easily and effectively.
- 1Considering the required energy supply, it is best to drink something containing 4-8% carbohydrates.
- 2In order to prevent fatigue due to exercise, aim to ingest 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour
- 3Before a game, after a game, or between games, it is necessary to replenish both water and carbohydrates, so an ionic beverage (sports drink) with about 6% carbohydrates is recommended.
Source: Japan Sport Association, Yokohama Sports Medical Center
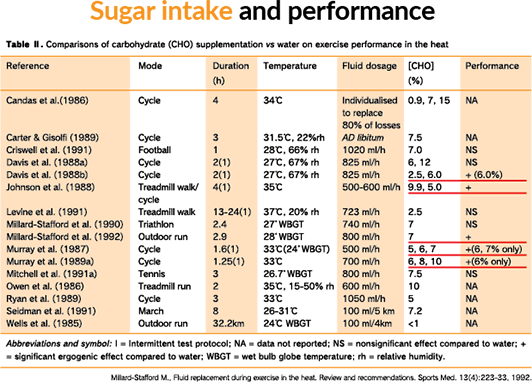
Increasing the amount of stored glycogen suppresses the breakdown of body protein
The amount of glycogen stored influences the breakdown of protein.
Having a large amount of glycogen in the body reduces the amount of urea nitrogen excreted in sweat, which is an indicator of the breakdown of body protein. Since glycogen in the muscles suppresses the breakdown of body protein, it is necessary to get enough sugar to preserve the protein used as an energy source.
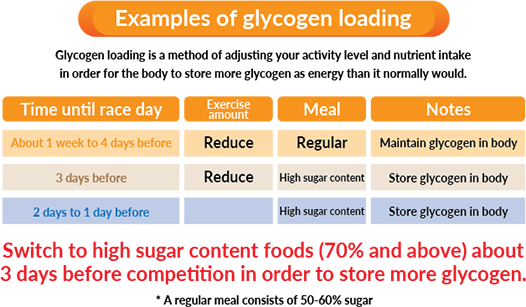
What is glycogen loading?
Glycogen loading is a method of storing glycogen, which becomes energy, in the muscles. It can be done by, for example, switching to a high-sugar diet (about 70% energy) 3 days before a game. It is an effective method for long-distance running or sports with a long game time.
For events that use more energy, have a plan to build up glycogen in the body based on the date of the event.